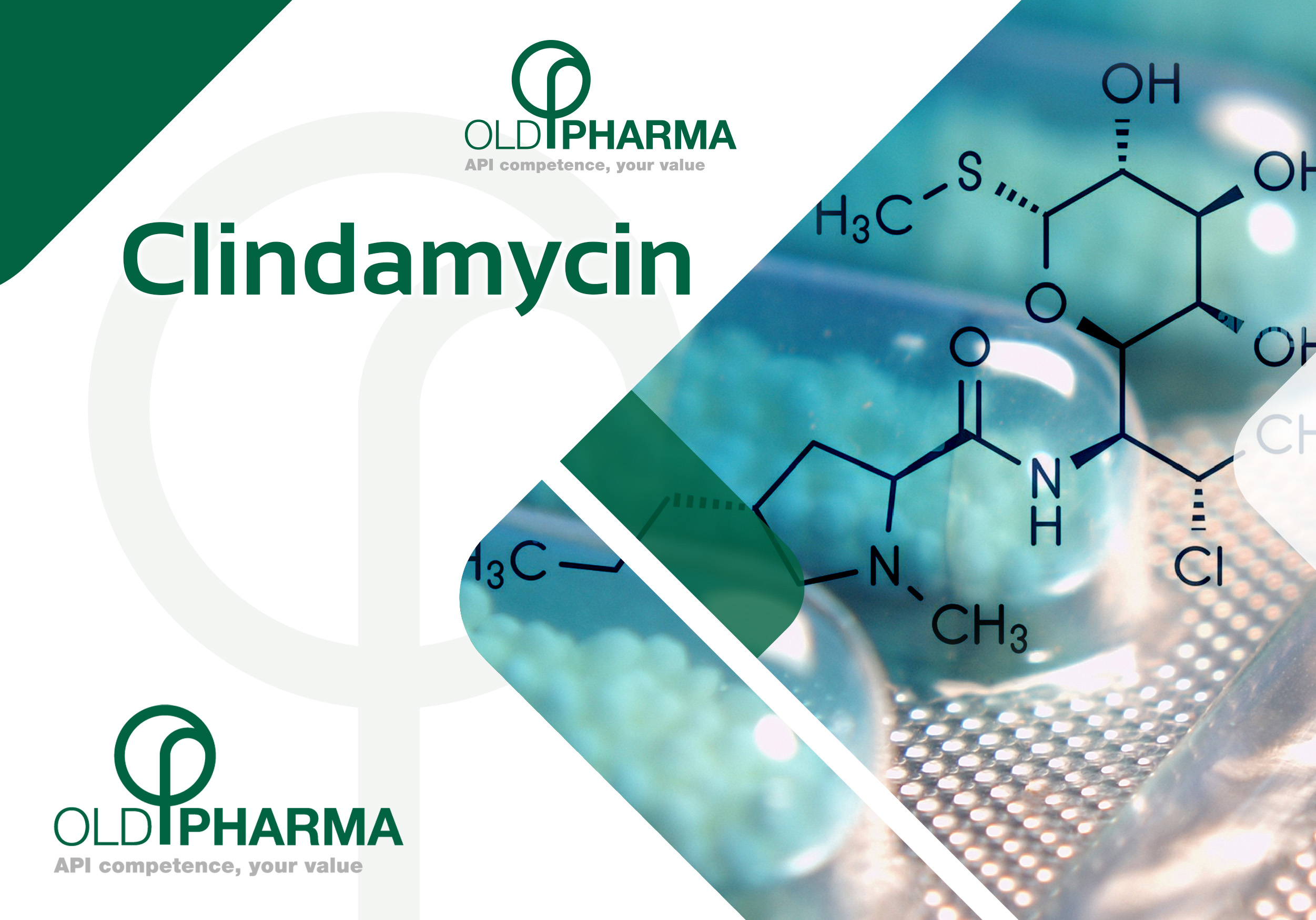
For those involved in the distribution and supply of APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients), clindamycin is a concrete example of how a well-established drug can continue to generate high-level industrial and therapeutic opportunities.

Within the landscape of mature antibiotics, few active ingredients have demonstrated the ability to remain as relevant as clindamycin. A historic molecule from the lincosamide class, it still holds a well-defined clinical role today, supported by new scientific evidence and increasingly targeted positioning within global antibiotic stewardship strategies.
A Distinctive Pharmacological Profile
Clindamycin works by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, inhibiting protein synthesis. This mechanism ensures proven efficacy against numerous Gram-positive and anaerobic bacteria, along with a unique ability to penetrate tissues, including the osteoarticular system and deep tissues.
Another point of interest for the industry is its ability to reduce toxin production in streptococcal and staphylococcal strains—a feature that remains invaluable in infections with a high toxin component. Recently, advanced cryo-electron microscopy studies have mapped the molecule’s binding with extreme precision, paving the way for increasingly rational and optimized applications.
Therapeutic Applications and New Formulations
Today’s market demands targeted antibiotic use to preserve effectiveness against antimicrobial resistance. In this context, clindamycin delivers maximum value in specialized areas:
- Dermatology: Triple-combination topical formulations (clindamycin, adapalene, and benzoyl peroxide) are demonstrating significant clinical superiority in acne treatment, with excellent patient tolerability.
- Bone and Prosthetic Infections: Clindamycin remains a reliable and well-documented option for treating complex bone tissue infections.
- Necrotizing Infections: Thanks to its antitoxin effect, the molecule retains a key adjuvant role in invasive Group A Streptococcus infections.
Industrial Excellence and API Quality
From an industrial perspective, demand for clindamycin remains stable and robust across all pharmaceutical forms: oral, parenteral, and topical.
At Old Pharma, we closely monitor the evolution of this API’s production. Today, the quality of the finished product depends more than ever on:
- Strict GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) standards.
- Full batch traceability.
- Impurity control in strict compliance with USP and EP monographs.
In a global market that rewards documented quality and manufacturing reliability, having a strategic partner for API supply is essential to successfully navigate scientific and regulatory developments.
Clindamycin is not simply an antibiotic from the past. It is a dynamic molecule, capable of generating new data and innovative formulations. For pharmaceutical companies, it represents a strategic asset that combines proven clinical efficacy with modern requirements for combating bacterial resistance.
References
Clindamycin: An overview – UpToDate
Clindamycin Hydrochloride Api Market CAGR, Size, Opportunities & Digital Trends 2026-2033 | LinkedIn